| Country | Code | Education | Literacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | AFG | 4.23 | 43.0 |
| Albania | ALB | 3.95 | 98.1 |
| Algeria | DZA | NA | 81.4 |
| Andorra | AND | 3.26 | NA |
| Antigua and Barbuda | ATG | NA | 99.0 |
| Argentina | ARG | 5.78 | 99.2 |
| Armenia | ARM | 2.81 | 99.7 |
| Aruba | ABW | 6.48 | 97.8 |
| Australia | AUS | 5.32 | NA |
| Austria | AUT | 5.50 | NA |
| Azerbaijan | AZE | 2.95 | 99.8 |
| Bahrain | BHR | 2.67 | 97.5 |
| Bangladesh | BGD | 2.47 | 73.9 |
| Barbados | BRB | 5.09 | NA |
| Belarus | BLR | 4.95 | 99.8 |
| Belgium | BEL | 6.54 | NA |
| Belize | BLZ | 7.38 | NA |
| Benin | BEN | 4.36 | 42.4 |
| Bermuda | BMU | 1.70 | NA |
| Bhutan | BTN | 7.39 | 66.6 |
| Bolivia | BOL | NA | 92.5 |
| Brazil | BRA | 6.24 | 93.2 |
| British Virgin Islands | VGB | 6.32 | NA |
| Brunei Darussalam | BRN | 4.43 | 97.2 |
| Burkina Faso | BFA | 4.17 | 41.2 |
| Burundi | BDI | 6.37 | 68.4 |
| Cabo Verde | CPV | 5.29 | 86.8 |
| Cambodia | KHM | NA | 80.5 |
| Cameroon | CMR | 3.07 | 77.1 |
| Central African Republic | CAF | NA | 37.4 |
| Chad | TCD | NA | 26.0 |
| Chile | CHL | 5.42 | 96.9 |
| China | CHN | NA | 96.8 |
| Colombia | COL | 4.50 | 95.1 |
| Comoros | COM | 2.49 | 58.8 |
| Congo, Dem. Rep. | COD | 2.17 | 77.0 |
| Congo, Rep. | COG | 4.56 | 80.3 |
| Costa Rica | CRI | 7.40 | 97.9 |
| Cote d'Ivoire | CIV | 5.39 | 47.2 |
| Cyprus | CYP | 6.38 | NA |
| Czech Republic | CZE | 5.79 | NA |
| Dominica | DMA | 3.39 | NA |
| Dominican Republic | DOM | NA | 93.8 |
| Ecuador | ECU | 5.00 | 94.5 |
| Egypt, Arab Rep. | EGY | NA | 71.2 |
| El Salvador | SLV | 3.96 | 88.5 |
| Eritrea | ERI | NA | 76.6 |
| Estonia | EST | 5.17 | NA |
| Eswatini | SWZ | NA | 88.4 |
| Ethiopia | ETH | 4.74 | 51.8 |
| Fiji | FJI | NA | 99.1 |
| Finland | FIN | 7.08 | NA |
| France | FRA | 5.46 | NA |
| Gabon | GAB | NA | 84.7 |
| Gambia, The | GMB | 2.06 | 50.8 |
| Georgia | GEO | 3.85 | 99.4 |
| Germany | DEU | 4.81 | NA |
| Ghana | GHA | 4.51 | 79.0 |
| Grenada | GRD | 10.24 | NA |
| Guatemala | GTM | 2.96 | NA |
| Guinea | GIN | 2.52 | NA |
| Guyana | GUY | 6.34 | NA |
| Haiti | HTI | 3.16 | 61.7 |
| Honduras | HND | 6.41 | 89.0 |
| Hong Kong SAR, China | HKG | 3.32 | NA |
| Hungary | HUN | 4.71 | NA |
| Iceland | ISL | 7.53 | NA |
| India | IND | NA | 74.4 |
| Indonesia | IDN | 3.58 | 95.7 |
| Iran, Islamic Rep. | IRN | 3.96 | 85.5 |
| Iraq | IRQ | NA | 50.1 |
| Ireland | IRL | 3.76 | NA |
| Israel | ISR | 5.85 | NA |
| Italy | ITA | 4.08 | 99.2 |
| Jamaica | JAM | 5.46 | NA |
| Japan | JPN | NA | NA |
| Jordan | JOR | 3.90 | 98.2 |
| Kazakhstan | KAZ | 2.98 | NA |
| Kenya | KEN | 5.36 | 81.5 |
| Korea, Rep. | KOR | NA | NA |
| Kuwait | KWT | NA | 96.1 |
| Kyrgyz Republic | KGZ | 6.59 | 99.6 |
| Lao PDR | LAO | NA | 84.7 |
| Latvia | LVA | 5.34 | NA |
| Lebanon | LBN | NA | 95.1 |
| Lesotho | LSO | 6.51 | NA |
| Liberia | LBR | NA | 48.3 |
| Lithuania | LTU | 4.22 | NA |
| Luxembourg | LUX | 3.96 | NA |
| Macao SAR, China | MAC | 3.08 | 96.5 |
| Madagascar | MDG | NA | 74.8 |
| Malawi | MWI | 5.61 | 62.1 |
| Malaysia | MYS | 4.97 | 93.7 |
| Maldives | MDV | 4.37 | 97.7 |
| Mali | MLI | 3.80 | 35.5 |
| Malta | MLT | 5.28 | 94.5 |
| Mauritania | MRT | 2.63 | 53.5 |
| Mauritius | MUS | 5.02 | 93.2 |
| Mexico | MEX | 5.24 | 95.4 |
| Micronesia, Fed. Sts. | FSM | 12.46 | NA |
| Moldova | MDA | 6.68 | NA |
| Monaco | MCO | 1.46 | NA |
| Mongolia | MNG | 5.18 | 98.4 |
| Montenegro | MNE | NA | 98.8 |
| Morocco | MAR | NA | 73.8 |
| Mozambique | MOZ | NA | 60.7 |
| Myanmar | MMR | 2.16 | 75.6 |
| Nepal | NPL | 5.16 | 67.9 |
| Netherlands | NLD | 5.48 | NA |
| New Zealand | NZL | 6.43 | NA |
| Nicaragua | NIC | 4.35 | 82.6 |
| Niger | NER | 6.02 | NA |
| Nigeria | NGA | NA | 62.0 |
| Norway | NOR | 7.98 | NA |
| Oman | OMN | 6.85 | 95.7 |
| Pakistan | PAK | 3.00 | 59.1 |
| Palau | PLW | NA | 96.6 |
| Panama | PAN | NA | 95.4 |
| Paraguay | PRY | 3.44 | 95.6 |
| Peru | PER | 3.97 | 94.4 |
| Philippines | PHL | NA | 98.2 |
| Poland | POL | 4.82 | NA |
| Portugal | PRT | 4.88 | 96.1 |
| Puerto Rico | PRI | NA | 92.4 |
| Qatar | QAT | 2.86 | 93.5 |
| Romania | ROU | 3.11 | 98.8 |
| Russian Federation | RUS | 3.83 | 99.7 |
| Rwanda | RWA | 3.75 | 73.2 |
| Samoa | WSM | 4.08 | 99.1 |
| San Marino | SMR | 3.04 | 99.9 |
| Sao Tome and Principe | STP | 5.08 | 92.8 |
| Saudi Arabia | SAU | NA | 95.3 |
| Senegal | SEN | 5.46 | 51.9 |
| Serbia | SRB | 4.04 | 98.8 |
| Seychelles | SYC | 4.42 | 95.9 |
| Sierra Leone | SLE | 4.64 | 43.2 |
| Singapore | SGP | NA | 97.3 |
| Slovak Republic | SVK | 4.64 | NA |
| Slovenia | SVN | 4.91 | NA |
| South Africa | ZAF | 6.16 | 94.4 |
| South Sudan | SSD | 1.50 | 34.5 |
| Spain | ESP | 4.27 | 98.4 |
| Sri Lanka | LKA | 3.48 | 92.4 |
| St. Kitts and Nevis | KNA | 2.61 | NA |
| St. Lucia | LCA | 5.80 | NA |
| St. Vincent and the Grenadines | VCT | 5.78 | NA |
| Sudan | SDN | NA | 60.7 |
| Suriname | SUR | NA | 94.4 |
| Sweden | SWE | 7.67 | NA |
| Switzerland | CHE | 5.11 | NA |
| Syrian Arab Republic | SYR | NA | NA |
| Tajikistan | TJK | 5.23 | NA |
| Tanzania | TZA | NA | 77.9 |
| Thailand | THA | NA | 92.9 |
| Timor-Leste | TLS | 5.29 | 68.1 |
| Togo | TGO | 5.11 | 63.7 |
| Tonga | TON | NA | 99.4 |
| Tunisia | TUN | 6.60 | NA |
| Turkey | TUR | NA | 96.2 |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | TCA | 3.16 | NA |
| Uganda | UGA | 2.77 | 76.5 |
| Ukraine | UKR | 5.41 | NA |
| United Kingdom | GBR | 5.61 | NA |
| Uruguay | URY | 4.87 | 98.7 |
| Uzbekistan | UZB | 7.08 | 100.0 |
| Vanuatu | VUT | 5.55 | 87.5 |
| Venezuela, RB | VEN | NA | 97.1 |
| Vietnam | VNM | 4.34 | 95.0 |
| West Bank and Gaza | PSE | 5.72 | 97.2 |
| Zambia | ZMB | NA | 86.7 |
Introduction to Statistics
STAT 120
Let’s do an introduction!
- Your name?
- What gender pronouns do you use?
- Favorite Scientist/Person?
- Recent fun memories?
What will you learn in this course?
- Analyzing data by doing exploratory data analysis
- Estimate some parameter of interest from the population
- Infer the population characteristics based in your estimation
- Quantify the uncertainty in the estimation
What will a typical day/week look like?
Before Class:
- Some reading to introduce some topics
- Daily quizzes
What will a typical day/week look like?
During Class:
- Mini-lectures
- Hands-on class activities
Statistics is distinct from mathematics
Statistics is the study of data and the uncertainties surrounding them. We will take a more conceptual route to statistics in this course.
What and Why of Statistics?
Science of collecting, describing, analyzing and making decisions based on data
- Sampling
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Inference
Allows us to make informed decisions in the face of uncertainty and let’s us take an unbiased and evidence-based viewpoint
Statistical Computation
- Statistical computing software called R
- RStudio/Posit gives a nice user-friendly interface to R
- R Markdown is a platform in Posit to write your codes and results
Data: Cases and Variables
Data are a set of measurements taken on a set of individual units
- These are cases or units
Data is stored and presented in a dataset that comprises of variables measured on cases
- A variable is any characteristic that is recorded for each case
EducationLiteracy dataset from Lock5
Each row = case & Each column = variable
Categorical Versus Quantitative
Variables are classified as either categorical or quantitative:
- A categorical variable divides the cases into groups. e.g. gender, country, state etc.
- A quantitative variable measures a numerical quantity for each case, e.g. age, height, sleep hours, blood pressure etc
Kidney cancer
Counties with the highest kidney cancer rates
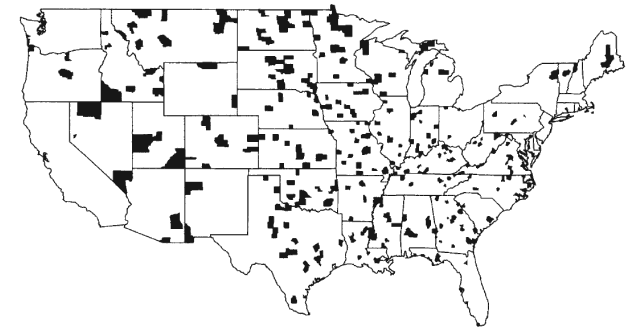
Source: Gelman et. al. Bayesian Data Anaylsis, CRC Press, 2004
Kidney cancer
If the cases in the kidney cancer dataset are people, then the measured variable is categorical
- We categorize each person as either having kidney cancer or not which is categorical.
Kidney cancer
If the cases in the kidney cancer dataset are counties, then the measured variable is quantitative
- Data collected at the county level is aggregated across all people living in the county. We then get rates of cancer which are numbers (quantitative).
Variable manipulations
Can use numbers to code categories of categorical variable
- e.g Gender (1 for male and 2 for female)
Can convert quantitative variable into categorical groups
- e.g. Income (0-50000 as Low, 50000+ as High)
Explanatory and Response Variable
When one variable helps us understand or predict values of another variable, we call the former the explanatory variable and the latter the response variable
Does meditation help reduce stress?
- explanatory variable: meditation
- response variable: stress level
Does sugar consumption increase hyperactivity?
- explanatory variable: sugar consumption
- response variable: hyperactive behavior
Group Activity 1
- Say hi to your neighbor
- Make a course folder called
stat120either on your Maize account or on your local computer - Please download the Class-Activity-1 template from moodle and go to class helper web page
10:00
