Sampling
STAT 120
Sampling and Inference
- A population includes all individuals or objects of interest.
- A sample is all the cases that we have collected data on (a subset of the population).
- Statistical inference is the process of using data from a sample to gain information about the population.
Sampling and Inference
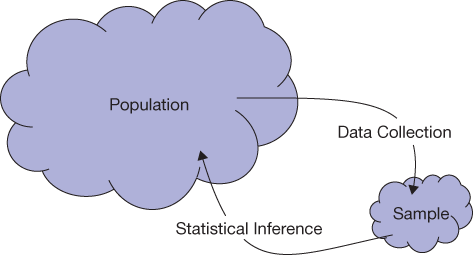
Population and Sample
MN Department of Natural Resources
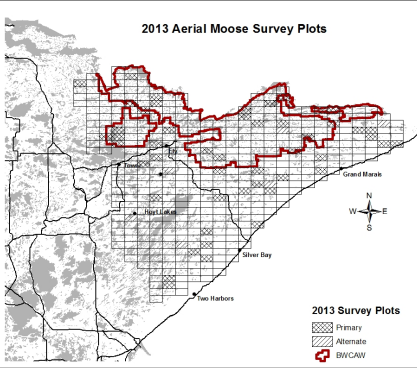
Population and Sample
MN Department of Natural Resources
- Population: all plots (grid cells) on the map
- Sample: the cross-hatched plots on the map
- Variable: number of moose counted in a plot
- Inference: estimated 2,760 moose in the entire population
Sampling Bias
Sampling bias occurs when the method of selecting a sample causes the sample to differ from the population in some relevant way
If sampling bias exists, we cannot trust generalizations from the sample to the population
To eliminate sampling bias always take a RANDOM SAMPLE!
Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address
“Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth, on this continent,
a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all
men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether
that nation,or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are
met on a great battle-field of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of
that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that
that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do
this. But, in a larger sense, we can not dedicate—we can not consecrate—we can
not hallow—this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have
consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will
little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what
they did here. It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the
unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It
is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us—that
from these honored dead we take increased devotion to thatcause for which they
here gave the last full measure of devotion—that we here highly resolve that
these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have
a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people,
for the people, shall not perish from the earth."Lincoln’s Gettysberg Address: What is the average word length?
Task: Select a sample of 10 words to estimate average word length of entire address
- Population? (describe cases of interest)
- Sample?
- pick your sample….
- variable measured?
- compute average word length
Group Activity 1
Go to the google form
Find the average word length and enter your answer
10:00
Bias in data
Even with a random sample, data can still be biased, especially when collected on humans
Some forms of bias
Some forms of bias to watch out for in data collection:
- Question wording
- Question order
- Context
- Non-response Bias
Question wording
A random sample was asked: “Should there be a tax cut, or should money be used to fund new government programs?”
| Tax Cut | Programs |
|---|---|
| 60% | 40% |
Question wording
A different random sample was asked: “Should there be a tax cut, or should money be spent on programs for education, the environment, health care, crime-fighting, and military defense?”
| Tax Cut | Programs |
|---|---|
| 22% | 78% |
Question order
Depending on the order of questions we can see either a greater differences in responses or lesser difference in response. Respondents tend to provide answers consistent with their prior responses.
Swedish Study: Response bias

Identified Sources of Bias in Swedish Study
Political Bias: The study experimentally primes the political affiliations of the respondents before asking questions about corruption. This bias arises when people’s political leanings affect their perception and reporting of corruption levels.
Sensitivity Bias: Questions about one’s experiences with corruption are sensitive in nature and may result in biased responses due to fear of retribution or social stigma.
Context
Ann Landers column asked readers “If you had it to do over again, would you have children?”
The first request for data contained a letter from a young couple which listed worries about parenting and various reasons not to have kids
\[30\% \text{ said yes}\]
Context
The second request for data was in response to this number, in which Ann wrote how she was “stunned, disturbed, and just plain flummoxed”
\[95\% \text{ said yes}\]
Non-response Bias
When respondents are either unable or unwilling to respond to your survey, then this results in a non-response bias
- Survey targeted to the wrong audience
- There is general unwillingness due to polar opposite opinions
- The survey did not reach the right respondent
e.g. A survey asking teenagers about best cigarette brands.
Group Activity 2

- Please download the Class-Activity-2 template from moodle and go to class helper web page
10:00